Treatment Considerations
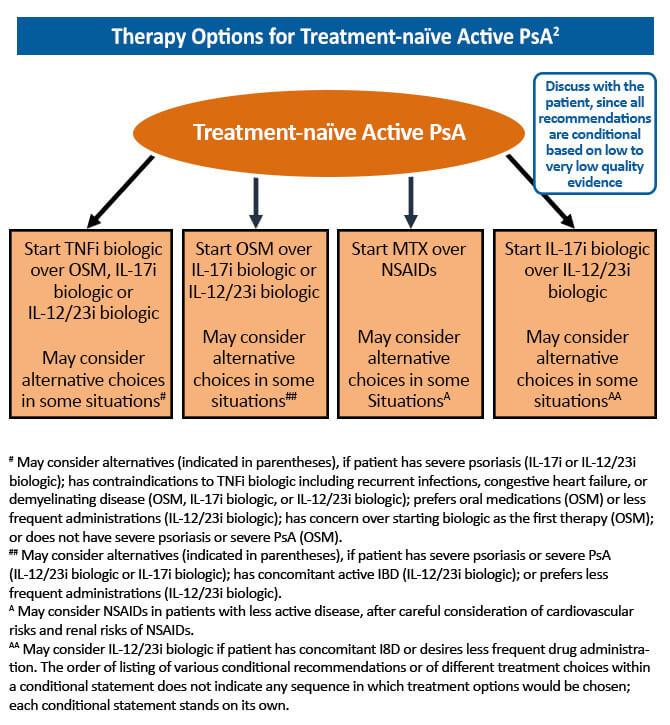
The goal of treatment for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) has evolved from merely pain and stiffness reduction to disease remission with the development of new treatments that target the underlying pathophysiology of the disease. A treat-to-target approach in the management of PsA has been shown to significantly improve joint outcomes for newly diagnosed patients. The benefit of tight PsA control was established in the TICOPA trial. In this study, treatment-naïve patients with early PsA (<24 month symptom duration) were randomized to tight control (review every 4 weeks and treatment escalation if minimal disease activity criteria not met) or standard care (standard therapy with review every 12 weeks). At 48 weeks, the odds of achieving a 20% improvement on the American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) scale were significantly higher in the tight control group compared to the standard care group (OR, 1.91; 95% CI, 1.03-3.55; P=0.0392). This study confirmed a significant benefit of tight control in terms of peripheral arthritis, skin disease, and patient reported outcomes.1 Current treatment guidelines recommend a treat-to-target strategy in the management of PsA, with the goal of achieving disease remission or minimal disease activity.2
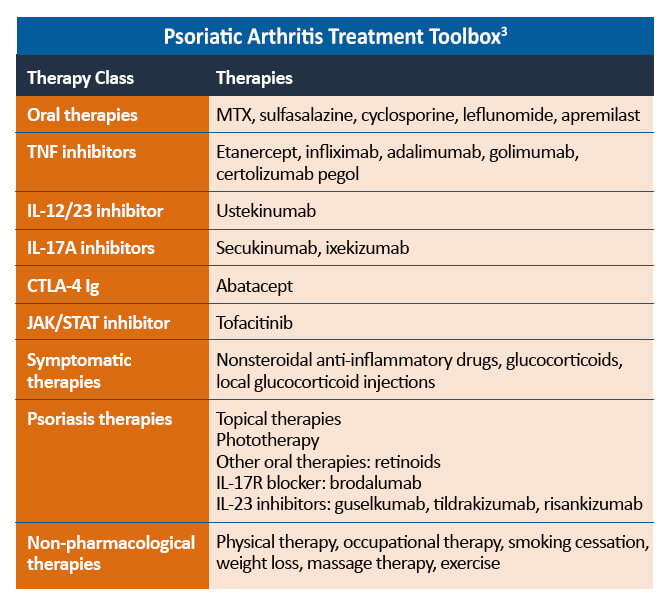
Treatment Considerations
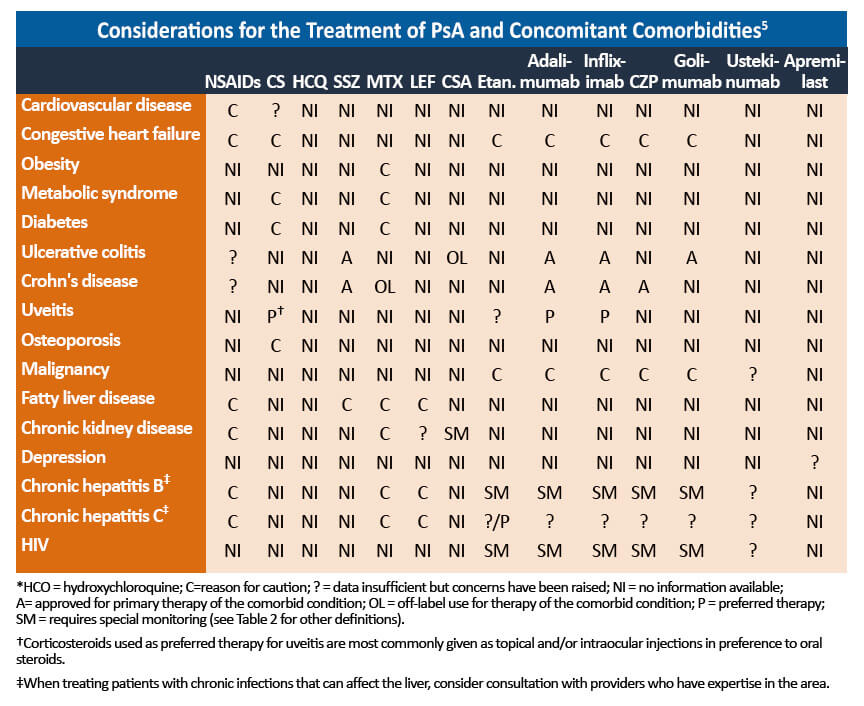
PsA is often complicated by associated comorbidities that should be taken into account when selecting treatment options.
- Interleukin 17 inhibitors can exacerbate disease in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and these agents should be avoided.4
- Etanercept should be avoided in patients with comorbid IBD.2
- Some TNF inhibitors are approved for the management of PsA, inflammatory bowel disease, and/or uveitis. These agents should be selected in patients with these comorbidities.4
- Steroids and DMARDs may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and liver abnormalities in patients with metabolic syndrome, a common associated comorbidity. 4
- Obesity is common in PsA patients and may limit the tolerance to therapies and increase the risk of progressive hepatic fibrosis. As obesity is associated with poorer clinical outcomes in patients with PsA, weight loss of 5%-10% should be encouraged to increase the probability of achieving MDA. 4
Close collaboration and communication with relevant specialists are crucial for the optimal management of PsA with related comorbidities. Psoriasis is present in most patients with PsA and should be addressed by a dermatologist. Extraarticular manifestations, such as inflammatory bowel disease and uveitis, are also a risk and gastroenterologists and ophthalmologists should be consulted to manage these comorbidities. 4
References
- Coates LC, Moverley AR, McParland L, et al. Effect of tight control of inflammation in early psoriatic arthritis (TICOPA): A UK multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;386:2489-2498.
- Singh JA, Guyatt G, Ogdie A, et al. 2018 American College of Rheumatology/National Psoriasis Foundation Guideline for the Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71:5-32.
- Ogdie A, Coates LC, Gladman DD. Treatment guidelines in psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(suppl 1):i37-i46.
- Van den Bosch F, Coates L. Clinical management of psoriatic arthritis. Lancet. 2018;391:2285-2294.
- Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, et al. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis 2015 Treatment Recommendations for Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:1060-1071.










